torsion of the appendix testes|What Is Appendix Testis Torsion? : trading Testicular torsion occurs in the testicle itself (not the appendix testis). The spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, becomes twisted and can cut off . O programa que muita gente conhece é a série com humanos e homens fantasias exibida nos anos 90, especificamente indo ao ar em 1997. O . Ver mais
{plog:ftitle_list}
23 de abr. de 2020 · Sometimes they used generic terms with the initials "C.P.," a common abbreviation for "child pornography," and code like "caldo de pollo," which means .
Differentiate between torsion of the appendix testis and other causes of acute scrotal pain, such as testicular torsion or epididymo-orchitis. Assess the severity and duration . Appendix testis torsion is a condition that affects the testes of the male reproductive system. This article looks at the symptoms and causes of this condition and .Torsion of the appendix testis is a twisting of a vestigial appendage that is located along the testicle. This appendage has no function, yet more than half of all boys are born with one. . Torsion of the appendix testis (occasionally called torsion of the hydatid of Morgagni) is the most common cause of an acute painful hemiscrotum in a child. The .
Testicular torsion occurs in the testicle itself (not the appendix testis). The spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, becomes twisted and can cut off . Two testicular appendages can undergo torsion and become symptomatic: the appendix testis and the appendix epididymis. The appendix testis, sometimes called . When the appendix testis undergoes torsion, a hard, tender nodule may be palpable on the upper pole of the testicle, and a blue discoloration referred to as the “blue dot . Torsion of testicular appendages can result in the clinical presentation of acute scrotum. Two such appendages are the appendix testis, a remnant of the paramesonephric (müllerian) duct, and.
Torsion of testicular appendages can result in the clinical presentation of acute scrotum. Two such appendages are the appendix testis, a remnant of the paramesonephric (müllerian) duct, .Testicular torsion, torsion of appendix testis, & epididymitis 39. the emergency department with a 2-day history of scrotal pain and was ultimately determined to have testicular torsion. He was initially diagnosed with epididymitis based on the .The appendix testis (or hydatid of Morgagni) is a vestigial remnant of the Müllerian duct, . If clinical suspicion is high for the serious differential diagnosis of testicular torsion, a surgical exploration of the scrotum is warranted. Torsion of the appendix of testis occurs at ages 0–15 years, with a mean at 10 years, which is similar .
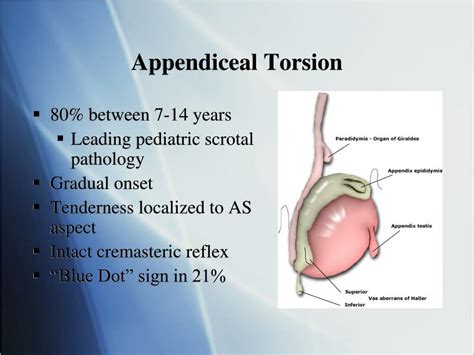
What is torsion of the appendix testis? The testicular appendage is a small amount of normal tissue, usually located on the upper part of a testis, left over from the time of testicular fetal development. Most boys will have it present at birth. Twisting of this appendix testis is called torsion of the appendix testis and it tends to occur in .The appendix testis is a small piece of tissue that is usually located on the upper part of the testis. The appendix epididymis is a small appendage located at the top of the epididymis (tube-shaped structure that connects to the testicle). Torsion means that this tissue has twisted. Because this structure serves no purpose, torsion does not . Torsion of the appendix testis . normal cremasteric reflex. normal testicular lie. positive blue dot sign. Treatment. Operative. orchiopexy (bilateral) indications. within 24 hours of disease onset. 4-8 hour window before there is permanent damage from ischemia.
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to it can be entirely blocked, causing damage more quickly. It's not clear why testicular torsion occurs. Most males who get testicular torsion have an inherited trait . The appendix testis, sometimes called hydatid of Morgagni, is a vestigial remnant of the Mullerian duct and is present in 76% to 83% of testes. When present, it is located on the superior pole of the testicle between the testis and epididymis and is the most common testicular appendage to undergo torsion. Two testicular appendages can undergo torsion and become symptomatic: the appendix testis and the appendix epididymis. The appendix testis, sometimes called hydatid of Morgagni, is a vestigial remnant of the Mullerian duct and is present in 76% to 83% of testes. [2]Testicular Appendage Torsion. Testicular appendage torsion is the twisting of a small piece of tissue above a testicle. The appendage doesn’t have a function in the body. But it can twist and cause pain and swelling that gets worse over time. It's not the same as testicular torsion.

What Is Appendix Testis Torsion?
The appendix testis is a small piece of tissue attached to the testicle. It is left over from before birth. It's a normal part of the system that creates female organs. Since it isn't needed in boys, it may disappear. But in many boys it remains attached. It serves no purpose, but it can become twisted (torsion).Torsion of any of the four testicular appendages [appendix testis (remnant of paramesonephric duct), appendix epididymis (remnant of the mesonephric duct), paradidymis (organ of Giraldes) and vas aberrans (organ of Haller)] may present with an acute scrotum, especially in children. 25 The appendix testis is usually located at the superior . Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. . Torsion of the appendix . Surgical treatment of torsion of the appendix testis is not mandatory but hastens recovery. Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and .
The testicular appendix is a small structure located at the upper pole of the testis and can cause acute scrotal pain when torsed.
Torsion of the appendix testis can usually be managed non-operatively with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [Jefferies, 2015; RCS, 2016; Radmayr, 2021]. Surgical exploration may be needed in people with persistent pain or in .
Introduction. Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord and its contents twists within the tunica vaginalis, compromising the blood supply to the testicle.. Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency, as without . How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.
Among children, torsion of the appendix testis or epididymis is an important cause of acute scrotum. It is most common in males aged 7–14 years [].Classic clinical signs of torsion of the appendage include a localized tender nodule at the superior testicular pole and a “blue-dot sign” (corresponding to the necrotic appendage).Testicular torsion is an emergency. It requires immediate referral to a surgeon; . The most common causes of acute scrotal pain and/or swelling are torsion of the testicular appendage (appendix testis), epididymitis and testicular torsion;
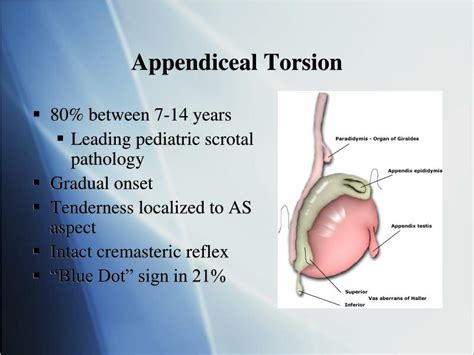
The cremasteric reflex is rarely intact in patients with testicular torsion but is usually present in patients with torsion of a testicular appendix. 2 A thorough testicular examination requires a .
Approximate Synonyms. Torsion appendix testis; Torsion of appendix of testis; ICD-10-CM N44.03 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 42.0):. 729 Other male reproductive system diagnoses with cc/mcc; 730 Other male reproductive system diagnoses without cc/mcc; Convert N44.03 to ICD-9-CM. Code History. 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New .
Our patient presented with appendix testis torsion and immediately after the surgery developed fever, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, hematologic and mucocutaneous findings. Torsion of the appendix testis is generally a self-limiting condition and the cause of scrotal pain in half of children 7–12 years of age. 5.Torsion of the appendix testis was confirmed intra-operatively. A small hypoechoic avascular lesion adjacent to an apparently enlarged epididymis is highly suggestive of torsion of appendix testis in a child with sudden onset of acute painful hemiscrotum. Distinguishing testicular torsion from torsion of the appendix testis by clinical features and signs in patients with acute scrotum Naoyuki Fujita,1 Mitsuhiro Tambo,1 Takatsugu Okegawa,1 Eiji Higashihara,2 Kikuo Nutahara1 1Department of Urology, 2Department of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) Research, Kyorin University School .
Torsion of testicular appendages can result in the clinical presentation of acute scrotum. Two such appendages are the appendix testis, a remnant of the paramesonephric (müllerian) duct, and the appendix epididymis, a remnant of the mesonephric (wolffian) duct. Torsion of testicular appendages can result in the clinical presentation of acute scrotum. Two such appendages are the appendix testis, a remnant of the paramesonephric (müllerian) duct, and the appendix epididymis, a remnant of the mesonephric (wolffian) duct.
Our patient presented with appendix testis torsion and immediately after the surgery developed fever, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, hematologic and mucocutaneous findings. Torsion of the appendix testis is generally a self-limiting condition and the cause of scrotal pain in half of children 7–12 years of age. 5.
bbcor bat compression test

Torsion of the appendix testis
Sumate a la evolución. Te presentamos una nueva forma de .
torsion of the appendix testes|What Is Appendix Testis Torsion?